Learn How to Use Google Keyword Planner is a powerful tool that can help you identify the best keywords for your website, blog, or online business. Whether you’re new to digital marketing or looking to refine your SEO strategy, understanding how to use Google Keyword Planner is crucial. In this guide, we’ll walk you through what Google Keyword Planner is, how to use it step-by-step, and why it’s beneficial for your keyword research needs.
What is Google Keyword Planner?
Google Keyword Planner is a free tool provided by Google that allows users to discover keywords and see their search volume, competition, and cost-per-click (CPC). It’s designed primarily for Google Ads, but it’s also incredibly useful for SEO. With this tool, you can find keyword ideas, analyze their performance, and create a list of keywords to target in your content.
Why Use Google Keyword Planner?
Before diving into how to use it, let’s understand why Google Keyword Planner is beneficial:
Discover Relevant Keywords: Find keywords related to your business or niche.
Understand Search Volume: See how often people search for specific keywords.
Analyze Competition: Identify how competitive keywords are in both paid and organic search.
Plan Your Content: Use keyword insights to create content that meets your audience’s needs.
How to Access Google Keyword Planner?
Step 1: Create a Google Ads Account
If you don’t already have a Google Ads account, you’ll need to create one. Go to Google Ads and sign up using your Google account. You don’t need to run an ad campaign to use Keyword Planner, but you do need an account.
Step 2: Navigate to Keyword Planner
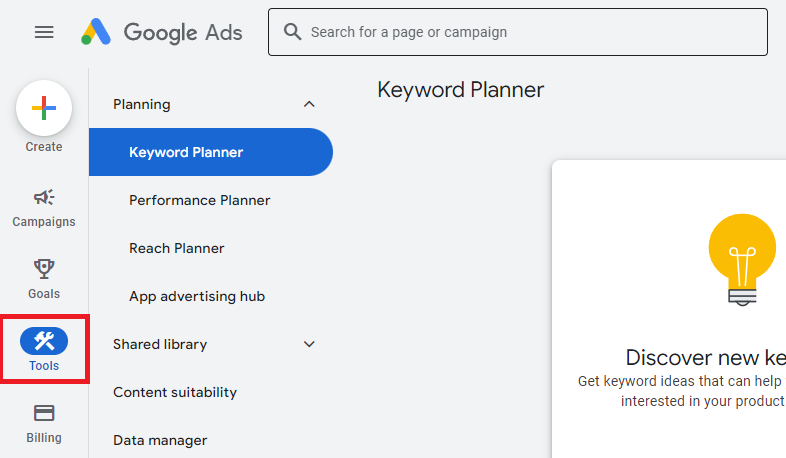
Once you’re signed in, follow these steps:
Click on the Tools & Settings icon (a wrench) in the upper right corner.
Under the “Planning” section, click on Keyword Planner.
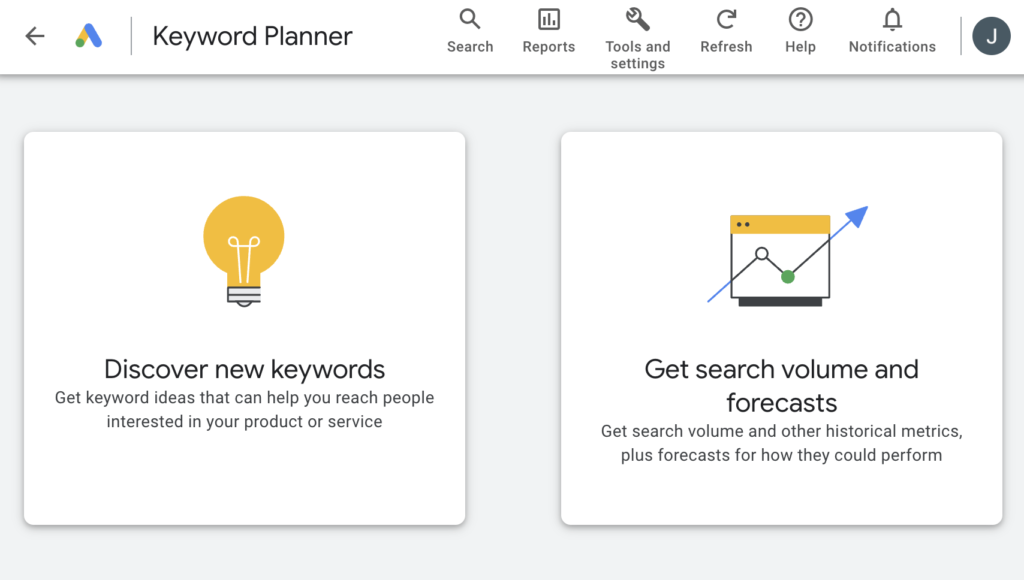
Step 3: Choose Your Tool:
Google Keyword Planner offers two main tools:
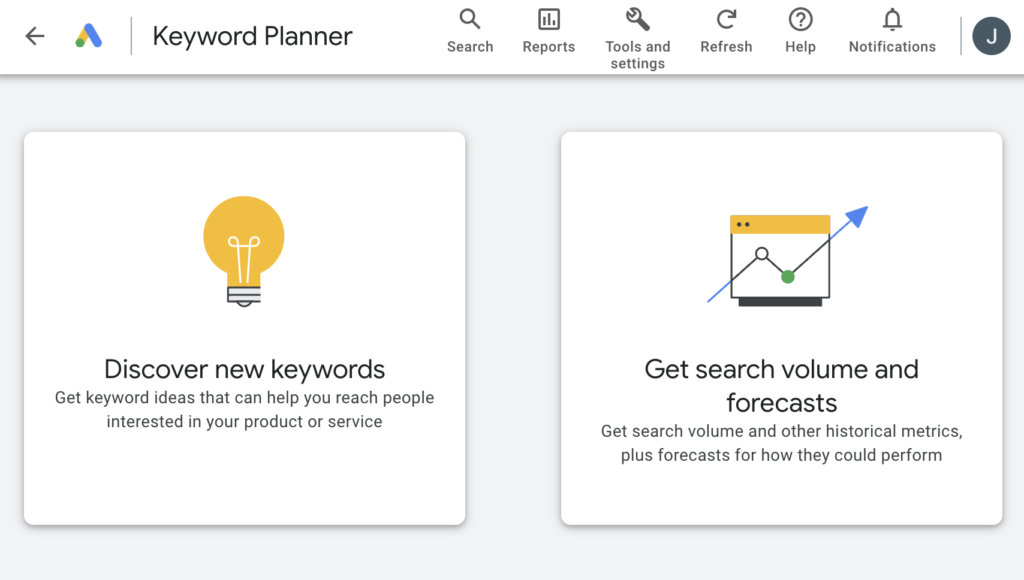
Discover new keywords: This tool helps you find new keyword ideas.
Get search volume and forecasts: This tool provides search volume data and forecasts for your selected keywords.
For this guide, we’ll focus on the “Discover new keywords” tool.
Step 4: Discover New Keywords:
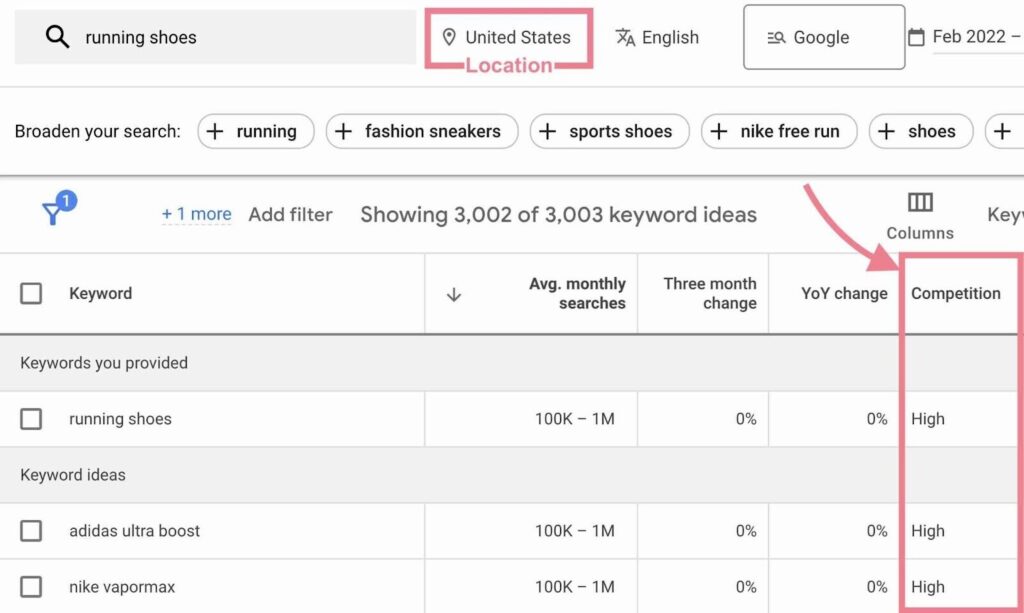
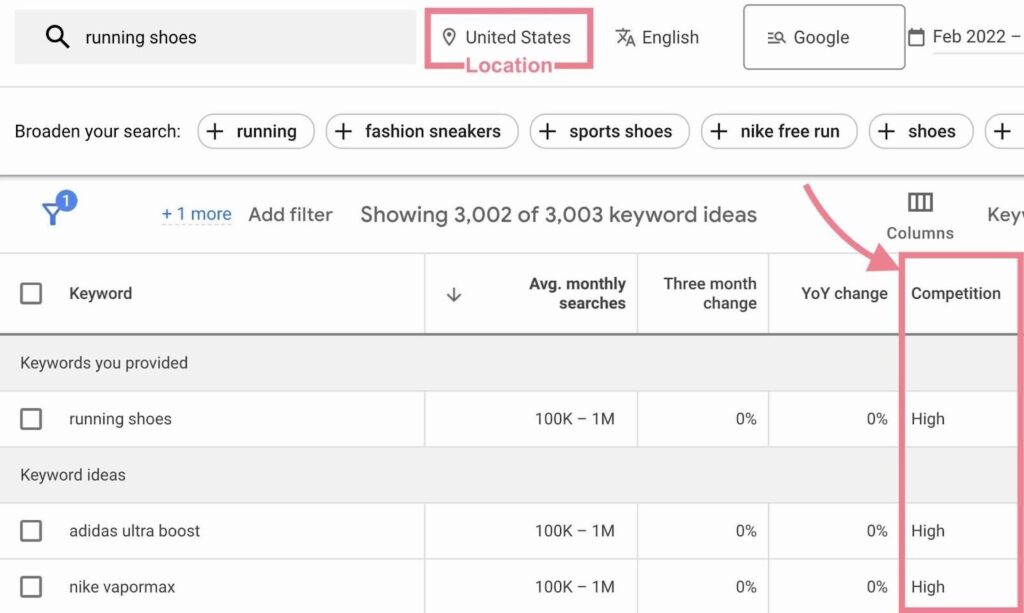
Enter Your Keywords or URL: In the “Discover new keywords” section, you can enter words or phrases related to your business. Alternatively, you can enter your website URL to get keyword ideas based on your site content.
Set Your Targeting: Choose the location, language, and search networks (e.g., Google and search partners) you want to target. This helps tailor the keyword suggestions to your specific audience.
Get Results: Click on Get Results to see a list of keyword ideas.
Step 5: Analyze Keyword Results:
Review the List: You’ll see a list of keyword ideas along with their average monthly searches, competition level, and top of the page bid range (for paid search).
Filter and Sort: Use filters to narrow down your list. You can filter by average monthly searches, competition, and more. Sort the results by clicking on the column headers.
Step 6: Refine Your Keyword List
Select Relevant Keywords: Check the boxes next to the keywords that are most relevant to your business.
Add to Plan: Click on the Add to plan button to save these keywords to your keyword plan.
Step 7: Use Your Keywords
Incorporate Keywords into Content: Use the selected keywords in your website content, blog posts, meta tags, and other on-page SEO elements. Ensure the keywords are used naturally and relevantly.
Monitor Performance: Regularly check how your keywords are performing. Use tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to track traffic, rankings, and conversions.
Tips for Effective Keyword Research:
How to Choose the Right Keywords?
Relevance: Ensure the keywords are highly relevant to your content and audience.
Search Volume: Target keywords with a good search volume to attract more traffic.
Competition: Balance between high and low competition keywords. High competition keywords are harder to rank for, while low competition keywords may not drive significant traffic.
Long-Tail Keywords: Include long-tail keywords (phrases with 3+ words) as they are more specific and often less competitive.
When to Conduct Keyword Research?
Before Creating Content: Conduct keyword research before writing new blog posts, articles, or web pages to ensure you’re targeting the right terms.
Regularly Update Keywords: SEO trends change, so it’s important to revisit your keyword strategy regularly and update your keywords as needed.
Competitor Analysis: Periodically analyze competitor keywords to find new opportunities and gaps in your strategy.
Why Monitor Keyword Performance?
Track Progress: Monitoring performance helps you understand which keywords are driving traffic and conversions.
Adjust Strategies: If certain keywords are not performing well, you can adjust your content or choose new keywords.
Stay Competitive: Regular monitoring keeps you competitive in your niche by adapting to changes in search trends and algorithms.
Steps for Using Google Keyword Planner: (In Sort Explanation)
Access Google Keyword Planner:-
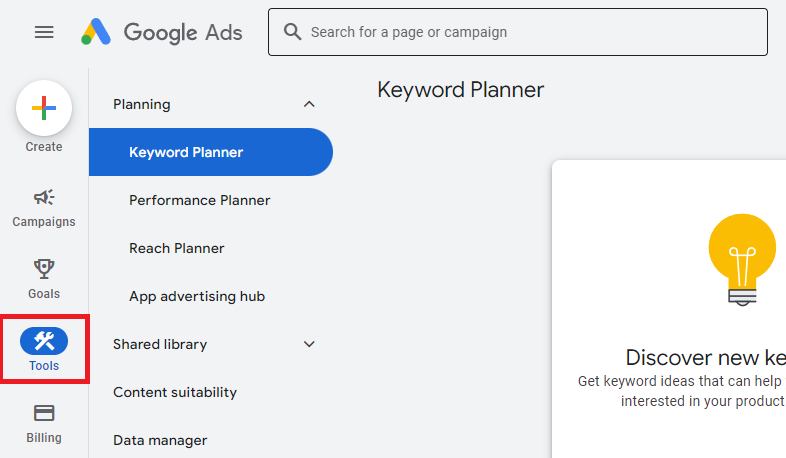
Sign in to Google Ads with your Google account.
Click on the Tools & Settings icon (a wrench) in the upper right corner.
Under the “Planning” section, click on Keyword Planner.
Choose Your Tool:
Select either Discover new keywords or Get search volume and forecasts. For finding new keywords, choose Discover new keywords.
Discover New Keywords:
Enter words or phrases related to your business or website URL.
Set your targeting by choosing location, language, and search networks.
Click on Get Results.
Analyze Keyword Results:
Review the list of keyword ideas with metrics like average monthly searches, competition, and top of the page bid range.
Use filters and sorting options to narrow down your list.
Refine Your Keyword List:
Select relevant keywords by checking the boxes next to them.
Click on Add to plan to save these keywords to your keyword plan.
Use Your Keywords:
Incorporate selected keywords into your content, meta tags, and other on-page SEO elements.
Monitor and adjust your keyword strategy using tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console.






